Biologi Struktur Sel
Cells are the smallest living units of
an organism. All cells have three things in
common no matter what type of cell they are. All cells have a cell membrane which separates the
inside the cell from its environment, cytoplasm, which is a jelly-like fluid, and DNA which is the cell's genetic
material. There are two broad categories of cells.
The first category is eukaryotic cells. They have organelles which include the nucleus and other
special parts. Eukaryotic cells are more advanced,
complex cells such as those found in plants and
animals. The second category is prokaryotic
cells.
They don't have a nucleus or membrane
enclosed organelles. They do have genetic material but it's
not contained within a nucleus. Prokaryotic cells are always one celled, or unicellular organisms, such as
bacteria. So what are organelles? Organelle means "little organ." Organelles are the specialized parts of a cell that have unique jobs to perform.
Let's start with the nucleus, the
control center of the cell. The nucleus contains DNA or genetic
material. DNA dictates what the cell is going
to do and how it's going to do it. Chromatin the tangled, spread out form of DNA
found inside the nuclear membrane.
When a cell is ready to divide DNA condenses into structures known as
chromosomes. The nucleus also contains a nucleolus, which is a structure where ribosomes
are made. After ribosomes leave the nucleus they will have the important job of "synthesizing", or making, proteins. Outside the nucleus the ribosomes and
the rest of the organelles float around in cytoplasm, which is the
jelly-like substance.
Ribosomes may wander freely within
the cytoplasm or attach to the endoplasmic
reticulum, sometimes abbreviated as ER. There are two types of ER: rough ER has ribosomes attached to it and smooth ER doesn't have
ribosomes attached to it. The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane enclosed passageway for
transporting materials such as the proteins synthesized by
ribosomes. Proteins and other materials emerge from the endoplasmic reticulum in small vesicles where the Golgi apparatus, sometimes called the Golgi body receives them.
As proteins move through the Golgi body
they're customized into forms that the cell can use. The Golgi body does this by folding the
proteins into usable shapes. Or adding other materials on to them such as lipids or carbohydrates Vacuoles are sac-like structures that store
different materials. Here, in this plant cell, the central vacuole stores water.
Going back to the animal cell, you'll see an organelle called a lysosome. Lysosomes are the garbage collectors that take in damaged or worn out cell parts. They are filled with enzymes that break
down this cellular debris. The mitochondrion in is an organelle
that is the powerhouse for both animal and plant cells.
During a process called cellular respiration the mitochondria make ATP molecules that provide the energy for all the
cells activities. Cells that need more energy have more mitochondria. Meanwhile the cell maintains its shape through a cytoskeleton. The cytoskeleton includes the thread-like microfilaments which are made of protein and microtubules which are thin hollow tubes Some organisms such as plans that are photoautotrophic meaning they capture sunlight for energy have cells with an organelle called
a chloroplast.
The chloroplast is where
photosynthesis happens It's green because it has a green
pigment called chlorophyll. Plant cells also have a cell wall
outside of their cell membranes that shape, support, and protect the plant cell. Animal cells never have a cell wall There are many other unique
structures that only some cells have. Here are just a few.
In humans, for example, the respiratory tract is lined with cells that have cilia. These are microscopic
hair-like projections that can move in waves. This feature helps trap inhaled particles in the air and expels them when you cough. Another unique feature in some cells is flagella.
Some bacteria have flagella. A flagellum is like a little tail that
can help a cell move or propel itself. The only human cell that has a flagellum is a sperm cell. In summary remember: eukaryotic cells are plant and animal cells with a nucleus and membrane-enclosed organelles While prokaryotic cells are unicellular organisms without these things.
All cells have a cell membrane, cytoplasm and genetic material. And even though only plant cells have
chloroplasts both plant and animal cells have mitochondria..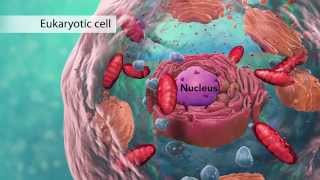
an organism. All cells have three things in
common no matter what type of cell they are. All cells have a cell membrane which separates the
inside the cell from its environment, cytoplasm, which is a jelly-like fluid, and DNA which is the cell's genetic
material. There are two broad categories of cells.
The first category is eukaryotic cells. They have organelles which include the nucleus and other
special parts. Eukaryotic cells are more advanced,
complex cells such as those found in plants and
animals. The second category is prokaryotic
cells.
They don't have a nucleus or membrane
enclosed organelles. They do have genetic material but it's
not contained within a nucleus. Prokaryotic cells are always one celled, or unicellular organisms, such as
bacteria. So what are organelles? Organelle means "little organ." Organelles are the specialized parts of a cell that have unique jobs to perform.
Let's start with the nucleus, the
control center of the cell. The nucleus contains DNA or genetic
material. DNA dictates what the cell is going
to do and how it's going to do it. Chromatin the tangled, spread out form of DNA
found inside the nuclear membrane.
When a cell is ready to divide DNA condenses into structures known as
chromosomes. The nucleus also contains a nucleolus, which is a structure where ribosomes
are made. After ribosomes leave the nucleus they will have the important job of "synthesizing", or making, proteins. Outside the nucleus the ribosomes and
the rest of the organelles float around in cytoplasm, which is the
jelly-like substance.
Ribosomes may wander freely within
the cytoplasm or attach to the endoplasmic
reticulum, sometimes abbreviated as ER. There are two types of ER: rough ER has ribosomes attached to it and smooth ER doesn't have
ribosomes attached to it. The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane enclosed passageway for
transporting materials such as the proteins synthesized by
ribosomes. Proteins and other materials emerge from the endoplasmic reticulum in small vesicles where the Golgi apparatus, sometimes called the Golgi body receives them.
As proteins move through the Golgi body
they're customized into forms that the cell can use. The Golgi body does this by folding the
proteins into usable shapes. Or adding other materials on to them such as lipids or carbohydrates Vacuoles are sac-like structures that store
different materials. Here, in this plant cell, the central vacuole stores water.
Going back to the animal cell, you'll see an organelle called a lysosome. Lysosomes are the garbage collectors that take in damaged or worn out cell parts. They are filled with enzymes that break
down this cellular debris. The mitochondrion in is an organelle
that is the powerhouse for both animal and plant cells.
During a process called cellular respiration the mitochondria make ATP molecules that provide the energy for all the
cells activities. Cells that need more energy have more mitochondria. Meanwhile the cell maintains its shape through a cytoskeleton. The cytoskeleton includes the thread-like microfilaments which are made of protein and microtubules which are thin hollow tubes Some organisms such as plans that are photoautotrophic meaning they capture sunlight for energy have cells with an organelle called
a chloroplast.
The chloroplast is where
photosynthesis happens It's green because it has a green
pigment called chlorophyll. Plant cells also have a cell wall
outside of their cell membranes that shape, support, and protect the plant cell. Animal cells never have a cell wall There are many other unique
structures that only some cells have. Here are just a few.
In humans, for example, the respiratory tract is lined with cells that have cilia. These are microscopic
hair-like projections that can move in waves. This feature helps trap inhaled particles in the air and expels them when you cough. Another unique feature in some cells is flagella.
Some bacteria have flagella. A flagellum is like a little tail that
can help a cell move or propel itself. The only human cell that has a flagellum is a sperm cell. In summary remember: eukaryotic cells are plant and animal cells with a nucleus and membrane-enclosed organelles While prokaryotic cells are unicellular organisms without these things.
All cells have a cell membrane, cytoplasm and genetic material. And even though only plant cells have
chloroplasts both plant and animal cells have mitochondria..

Comments
Post a Comment